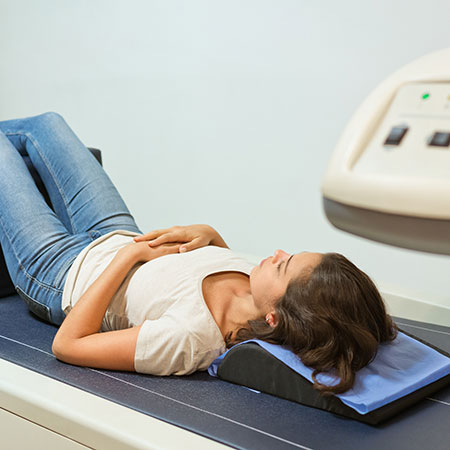
DEXA Bone Densitometry
A Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) test is a bone density study used to determine whether you have osteoporosis or low bone mass, conditions that commonly affect women after menopause and, in some cases, men. It is a fast, safe and painless test that measures bone strength and can predict your risk for bone fracture. DXA may also be used as a follow-up procedure to monitor response to specific medications.