Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
A less invasive way to treat uterine fibroids
What are uterine fibroids?
- They are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that grow on or within the lining of the uterus.
- They can range in size from as small as a grape to as large as a cantaloupe.
- Approximately 20-40% of women over age 35 have fibroids.
- African-American women are three times more likely to develop them.
What are the Symptoms?
Fibroids can result in:
- pelvic pain or discomfort
- urinary incontinence
- frequent urination
- heavy menstrual bleeding
The location and size of uterine fibroids can affect the severity of these symptoms and impact your quality of life. Fibroids are also hormonally sensitive, so the symptoms can be cyclical, just like with menstruation.
What are My Treatment Options?
If your fibroids are not causing pain or other symptoms, treatment is not necessary. Your OB/GYN might wish to monitor their growth during annual examinations. If symptoms are more severe, options include:
- Hormone treatment medication. This can help relieve symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure, but cannot eliminate fibroids. Medication can also cause side effects, such as weight gain, vaginal dryness and infertility.
- Surgery, in the form of hysterectomy (removal of the entire uterus) or myomectomy (removal of fibroids from within the uterus) are options that are used today.
Hysterectomy is the most common procedure to treat fibroids. However, this surgery is expensive, requires a six-week and sometimes painful recovery and can result in scarring. What’s more, new research has demonstrated significant long-term health risks associated with hysterectomy. These include a significantly higher risk of heart disease, as well as increased risk of certain cancers, incontinence, weight gain, early menopause (even without ovary removal), depression and sexual dysfunction. 1,2,3,4,5
Myomectomy is the preferred treatment for women who wish to become pregnant, and/or to improve their chances for becoming pregnant. However, fibroids often return within a few years of having this procedure.
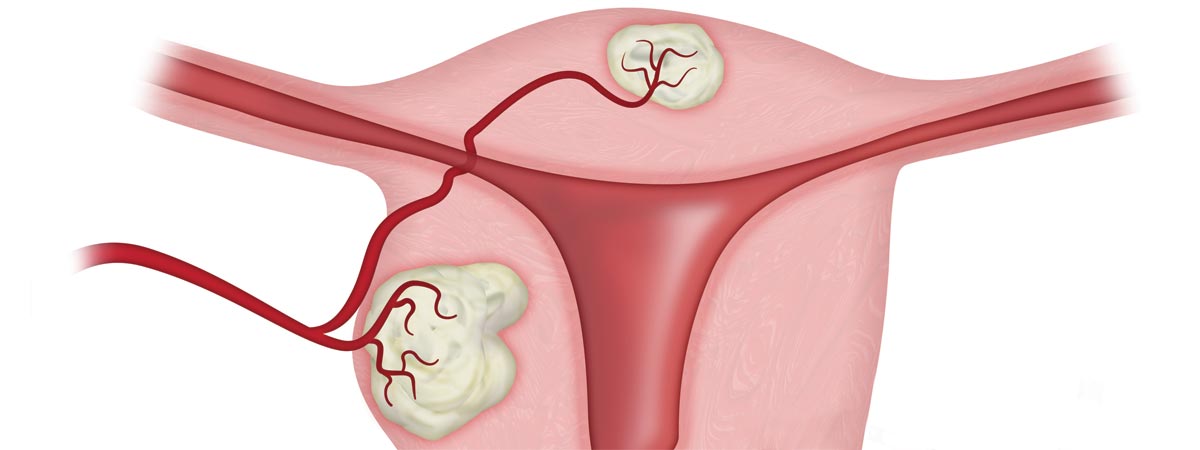
- Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE). This less invasive, FDA-approved and highly effective approach for treating fibroids is performed by a specialized doctor called an interventional radiologist, who uses X-ray imaging to guide a catheter through the femoral artery in the groin to the uterine artery. When the catheter has reached the location of the fibroids, the radiologist embolizes or “blocks” the blood vessels that feed the fibroid, depriving it of oxygenated blood. The fibroid then shrinks and the symptoms gradually disappear.
UFE is performed on an outpatient basis. It takes less than an hour, and the patient may return home within 24 hours after the procedure.
Is UFE right for me?
You may be a candidate for uterine fibroid embolization if you:
- Are experiencing the symptoms of uterine fibroids
- Are not or no longer wish to become pregnant
- Are seeking an alternative to hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
- Wish to avoid surgery or are a poor candidate for surgery
About the procedure
UFE is a safe, proven and minimally-invasive treatment for uterine fibroids. A specially trained interventional radiologist uses imaging guidance to thread a small catheter through your body to the site of the blood vessel feeding the fibroids. The vessel is then blocked, causing the fibroids to shrink and reduce the symptoms they are causing. The procedure is performed in about an hour, requires only a small nick in the skin, and patients can return home within 24 hours.
Benefits of UFE
Women who undergo UFE have reported a high level of satisfaction and a significant improvement to their quality of life. Compared with surgical hysterectomy, UFE carries less risk, requires a shorter hospital stay and the patient can resume normal activities faster