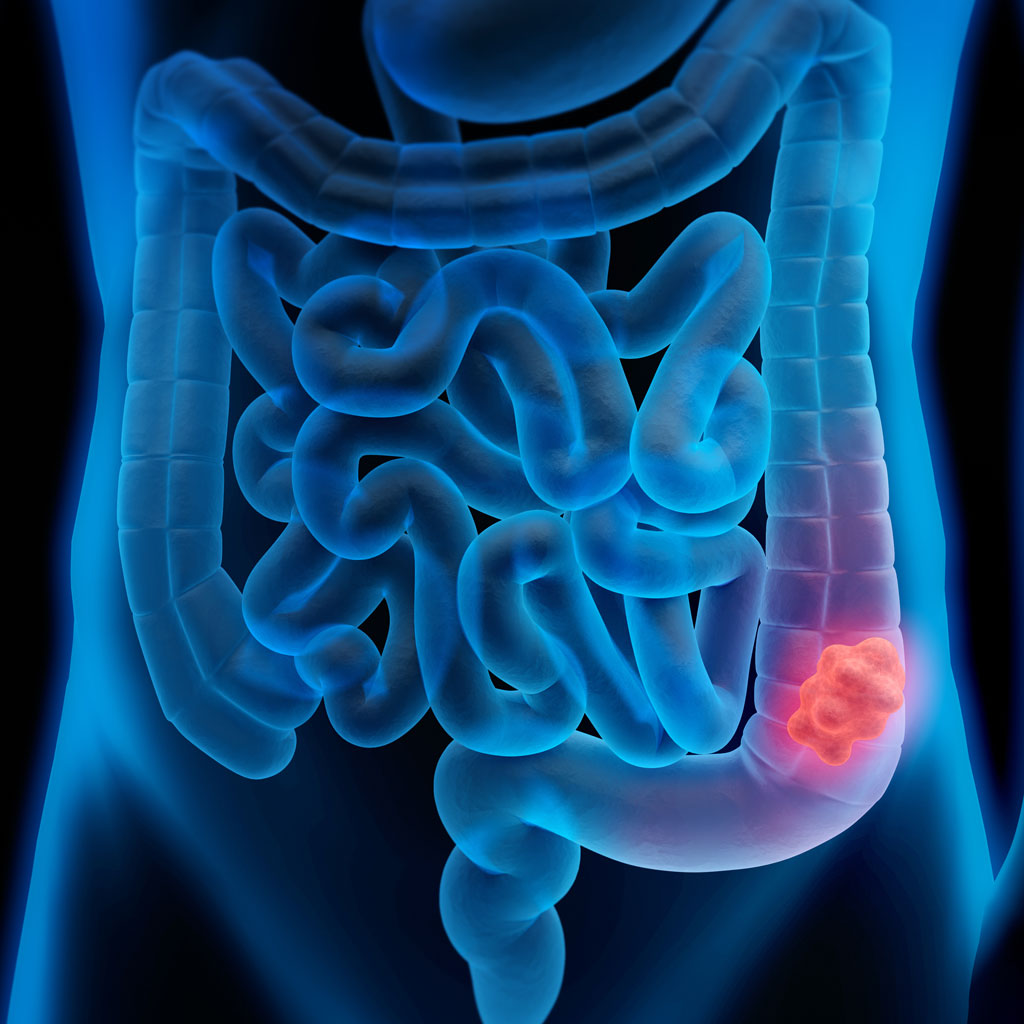
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the colon or rectum, typically from abnormal growths called polyps. This form of cancer can affect both men and women and is one of the most prevalent types of cancer worldwide. Arming yourself with the knowledge of the signs, risks, and significance of early screening is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer develops when cells in the lining of the colon or rectum begin to grow uncontrollably. Most colon cancers begin as benign polyps, which over time can turn cancerous. Symptoms may not appear in the early stages, making routine screenings essential.
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for the number of colorectal cancers in the United States for 2024 are:
- About 106,590 new cases of colon cancer (54,210 in men and 52,380 in women)
- About 46,220 new cases of rectal cancer (27,330 in men and 18,890 in women)
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Early signs of colon cancer can be subtle or non-existent, which underscores the importance of regular screenings. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include changes in bowel habits, persistent abdominal discomfort, blood in stool, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or a feeling that the bowel doesn’t empty completely.
Statistics
Colon cancer is a significant health concern globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Each year, millions of new cases are diagnosed worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for prevention and early detection strategies.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing colon cancer. Age is a key factor, with the majority of cases occurring in individuals aged 50 and older. A personal or family history of colon cancer or polyps, inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, a diet high in processed meats and low in fiber, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption are also associated with increased risk.
Importance of Early Screening
Early detection through regular colon cancer screenings such as colonoscopies significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Colon cancer often develops slowly, allowing for the detection and removal of precancerous polyps before they become malignant. Screening tests can also identify cancer in its early stages when treatment is most effective and the likelihood of a complete recovery is highest.
Types of Screening
Several screening methods are available for colon cancer detection, including colonoscopy, fecal occult blood tests (FOBT), fecal immunochemical tests (FIT), and stool DNA tests. The American Cancer Society recommends regular screenings starting at age 45 for average-risk individuals, and earlier for those with specific risk factors or family history.
Colon cancer is a significant health issue with potentially serious consequences if not detected and treated early. Understanding the risk factors and recognizing potential symptoms are essential steps toward prevention and timely intervention. While age and family history play a role in risk, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fiber, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can contribute to lowering the risk of developing colon cancer.
Advanced Medical Imaging Consultants services many locations that offer diagnostic imaging for your diagnostic imaging needs. If you would like to learn more please give our office a call at 970-484-4757.